Levels of Evidence/Sources of Evidence
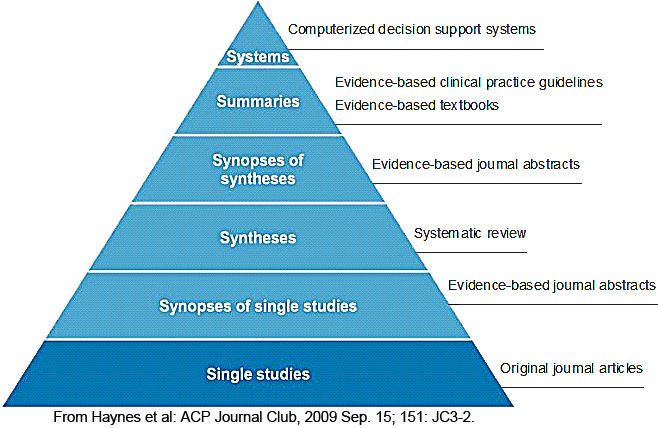
Summaries
These include clinical pathways or textbook summaries that integrate evidence-based information about specific clinical problems and provide regular updating.
National Guideline Clearinghouse
Syntheses
Systematic reviews are critically appraised syntheses of the best evidence on an individual question. Several organizations create systematic reviews; the most well known is the Cochrane Collaboration. Well-done systematic reviews gather the best studies, usually randomized controlled trials, using a detailed and comprehensive search strategy. They identify those studies of the best quality that ask similar questions and appraise them in a systematic way.
The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
The Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effect (DARE)
Systematic Reviews are also searchable in MEDLINE:
Ovid MEDLINE: Systematic Reviews
Single studies
Original research studies still have great value in the EBP model. The key is being able to identify the best evidence from the millions of articles published. In databases like PubMed and CINAHL searchers can employ Clinical Query search tools or limit to individual publication types.
The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews
Adapted from Houser J, Oman KS. (2011). Evidence-based practice: an implementation guide for healthcare organizations. Sudbury, Mass: Jones and Bartlett Learning, p.179-180.